--Author:ViewDAO.DaPangDun、ViewDAO.zhihong、ViewDAO.realAlitta
NOTE: The article is very long, if you are not interested in the introduction of the projects, you can skip that part.
1、Introduction
With the popularity of the metaverse concept, NFT (Non-Fungible Token) has become one of the hot spots in 2021, and the NFT market has gradually become a very important field. According to NFT data company Nonfungible.com:
- The scale of NFT transactions in 2021 will reach 17 billion US dollars, and only 82 million US dollars in 2020, an increase of about 210 times.
- The number of cryptocurrency wallets belonging to NFT users (those who hold or trade NFTs) in 2021 has exceeded 2.5 million, up from 89,000 a year ago. Number of buyers increased from 75,000 to 2.3 million.
- The current total market value of the NFT market is about 17 billion US dollars, accounting for ~1% of the total cryptocurrency market.
Of course, with the development of NFTs, a very important problem gradually emerged:
[NFT's liquidity problem]: In any product in the financial market, liquidity occupies an extremely important position.
2、Thinking and Analytical Process (Team)
After seeing this topic, my two friends (zhihong, realAlitta) and I are going to conduct detailed research according to the following steps:
- Brainstorm (preliminary discussion)
- Collect and review relevant data and information
- Organize information, build and think frame
- Discuss again, think and judge
- Document preparation
In this article, I will take everyone to participate in the specific analysis and thinking process of this issue, and I will try my best to use simple language to analyze the corresponding analysis ideas.
2.1 Analysis topic
First of all, we clarify the content of the subject: the liquidity problem of NFT. Specifically, it contains two meanings:
- The problem of low liquidity of NFTs
- Problems caused by low liquidity of NFTs
In fact, it needs to be clarified here that compared to traditional art auctions (of course, the current NFT is far more than just art collections), the liquidity of NFTs in the Crypto market has been greatly improved.
Let's analyze one by one👇👇👇
2.1.1 Reasons for low NFT liquidity
We can think about this problem from a simple cognition (here you may wish to think about it yourself), the possible reasons are:
- Don't know what NFT is
- Don't think NFTs will be valuable in the future
- Know NFT, but don't know how to participate
- The price is too high to afford it, and eventually it becomes a game for a small number of people
- NFT lacks sufficient expansion applications (this one may be difficult to understand, but you can refer to the ecological model of the currency circle, that is, a field itself needs to have enough ecological or financial products to easily generate higher liquidity)
It may be that there are few channels (compared to the few exchanges in the currency circle at the beginning), or the threshold for participation is too high (for example, there are still many people who do not know how to use wallets)
2.1.2 Problems caused by low NFT liquidity
The main question is:
- The utilization rate of assets by NFT holders is very low (the realization cycle is usually long and very inflexible)
- Holders do not have enough hedging means (such as BTC, we are worried about falling, and hedging can be used to hedge)
2.2 think of solutions
We can still think about solutions according to our existing knowledge until we have thoroughly investigated the project in the market. Usually, the solution discussed in this way is not accurate, but it will greatly improve the researcher's ability to think deeply and independently, and it will also help the researcher to make their own knowledge framework more complete.
Let's analyze the above reasons one by one👇👇👇
2.2.1 NFT流动性低的原因解析和措施分析
For points 1 and 2 <<<
[Analysis]: This is a cognitive problem, and it is necessary to popularize the meaning, connotation and value of NFT to the public
[Measures]: Traditional or Internet propaganda, evangelists who have formed a firm belief in NFT, a large number of popular science materials or introduction videos, wealth-making effect or out-of-circle effect, celebrity effect, etc.
For point 3 <<<
[Analysis]: This is a participation issue. It requires as many participating platforms as possible, and the interactive experience is as simple as possible. We can refer to the relevant experience of homogenized tokens.
[Measures]: Develop a variety of NFT trading platforms, and gradually improve the interactive experience of NFT trading. Further, we can also develop NFT transaction aggregators similar to various wallets
For point 4 <<<
[Analysis]: At present, the price of head NFTs (such as CryptoPunks) is indeed far from the scope that ordinary people can participate in, but there are also a large number of low-priced NFTs
[Measures]: Whether crowdfunding can be used to collectively purchase high-value NFTs, or whether high-value NFTs can be converted into many small shares, so that the value of each share may be within the affordable range of the public. (Of course, this may involve issues such as NFT rights)
For point 5 <<<
[Analysis]: This is the financialization of NFT. After financialization, liquidity can be mobilized through many financial products. You can refer to DEFI.
[Measures]: Is it possible to think about the organic combination of NFT and DEFI to generate more financial products of NFT, or to carry out a more in-depth combination with GAMEFI, Metaverse, etc.
2.2.2 Analysis of the problems caused by the low liquidity of NFT
Parse:
The general income method of NFT holders is to buy low and sell high, but because the cycle of NFT transactions is relatively long, the efficiency of obtaining income is relatively low. So if we want to increase its revenue potential, we need to refer to the existing model of the currency circle. As mentioned above: a good reference is the various financial products in DEFI. DEFI greatly liberates the extension value of the currency, which can bring a lot of additional benefits to the holders. At the same time, DEFI currently has relatively mature paths and solutions. Therefore, we can consider how to organically combine NFT and DEFI to achieve additional holding benefits for NFT holders.
>>>Loan<<<
The most common DEFI product is [lending], so let's think about the general scheme of NFT lending:
- Pledge NFT to the lending platform, and agree on parameters such as time and interest
- Lend a certain amount of stablecoins or other currencies, so that you can use part of the value of the NFT to do many other things (such as entering the market to participate in speculative transactions, etc.)
- Then from the perspective of the source of funds, it may be an individual, or it may be organized by a fund or DAO, then it is possible to form two modes of peer-to-peer or peer-to-pool
So what is an important question here?
Yes, how much can you borrow? This requires everyone to have a common understanding of the pricing of specific NFTs, and at the same time, it is necessary to avoid the exchange of a large number of truly valuable digital currencies caused by junk NFTs due to inaccurate pricing.
>>>Lease<<<
At present, more and more NFTs not only have "artistic value", but also carry a lot of rights (such as airdrops, memberships, tickets, etc.), so this provides the possibility for [leasing]:
- NFT holders pledge NFT to leasing platforms
- The lessor leases the NFT, agrees on parameters such as time and interest, and pays the deposit
- The lessor realizes certain rights and interests through NFT
- Return the NFT and pay the corresponding interest
>>>Derivatives<<<
First of all, it is emphasized that many people have an incorrect understanding of derivatives and think that the derivatives market is a market for people who are serious about gambling. In fact, financial derivatives can not only meet the needs of customers for accurate pricing and flexible hedging, but also effectively increase Market liquidity, reducing transaction costs, is conducive to improving the investment and financing functions of the capital market, and at the same time improving the flexibility of the financial market.
Common derivatives include: contracts, options, insurance, funds
Contracts or Options: Building NFT-based contracts, which requires a continuous NFT price mechanism (oracle) and automated market makers that provide sufficient depth.
Insurance: According to the value of the NFT, the NFT is insured for theft, loss, etc. The model may be the same as our traditional insurance model, but it is necessary to introduce clauses for the characteristics of the NFT.
Funds: "index funds" can be established based on the value of different NFTs, or a foundation (similar to DAO) can be established with NFTs and then invested, etc.
>>>Convert<<<
Diverging our brains, we know that there are many ways to promote liquidity in traditional homogenized tokens, so can it be used directly in NFT? !
If we can have a way to convert NFT into a specific homogenized token, then it will be easy later, and we can do a lot of liquidity operations through traditional methods. This is also a very interesting idea.
So let's summarize now, to improve the liquidity of NFT, the main measures we have initially thought about include:
- Invest more funds and more people into the NFT market area
- Build more NFT trading platforms
- Establish an NFT aggregation trading platform
- NFT crowdfunding
- NFT fragmentation
- NFT*DEFI: NFT lending platform
- NFT*DEFI: NFT rental platform
- NFT*DEFI: NFT derivatives
- Convert NFTs into homogenized tokens, and then perform operations to increase liquidity
2.2.3 Think further
Through the above analysis, in fact, many measures need a very important point, have you found it?
Yes, it is the price of NFT, to be precise, it is the pricing mechanism of NFT.
Because of its particularity (non-homogenization), NFT is difficult to have a relatively strong continuity in price like homogenized tokens. However, if there is no better price mechanism, then many measures to increase liquidity will not be easy to operate (such as lending: how can I measure how much this NFT can borrow, and how much is the value of over-collateralization appropriate?)
OK, the problem has arisen, let's think about it first:
How to price a product?
…………
>>>1、Manual bidding<<<
- Buyout price: Just like selling vegetables in the market, make a price, and others will buy it if they think it is suitable
- Auction: Like the auctions in Xiuxian novels that we often read, usually the highest bidder wins. Of course, there is still a "lottery auction" in the NFT market, if you are interested, you can learn about it.
Scope of application:
- Main NFT trading platforms (order mode, auction mode)
- Peer-to-peer or peer-to-pool lending
- peer-to-peer rental
In this way, the price of NFT mainly depends on the judgment of the participants, and its enhancement of liquidity is not particularly large.
>>>2、Automatic quotation mechanism<<<
If you want to achieve automatic quotation, you need to have a price determination rule, which is converted into a part of the smart contract to execute. Such a price mechanism is very similar to the "oracle machine (typically representing ChainLink)" in DEFI, and there are many forms of implementation:
NFTs are often in series, so the entire series will have many different prices. (analogous to an array, what data is used to measure this array) There are several ideas:
- [Lowest price]: It is called Floor Price in NFT. The floor price can be used as the target, then relatively speaking, the liquidation of the entire NFT in the field of lending and other fields will be much safer (equivalent to this NFT, I have identified it with the lowest price, and then I can control the amount of over-collateralization. Safer to control liquidation risk)
- Of course, the problem with the lowest price is that the value of high-worth NFTs is greatly underestimated (for example, my CryptoPunks is worth 100E, and the floor price of the entire series is 10E. If you measure the value of my NFTs according to 10E, it must be greatly underestimated) , which will result in a low willingness to participate in high-worth NFT holders. A possible solution is to divide the entire series into several series, such as Punks low-value series, Punks medium-value series, and Punks high-value series for optimization.
- [Weighted average price]: The weighted price can be calculated by weighting the price of the NFT. The weighted price is relatively neutral, reflecting the price of the NFT that falls within the larger probability area. The price obtained in this way may be more reasonable for the valuation of the NFT. . But the problem it brings is that the risk of liquidation increases, and if the amount of high-net-worth NFTs is too different from others, the calculated price will deviate too much.
- [Algorithmic pricing]: We think that we can comprehensively calculate the price, trend, transaction volume and other data of each NFT in the series through big data or AI technology, and then obtain a price through an algorithm. The advantage of the price that can be obtained by this calculation method is that it has continuity, and may develop a more valuable NFT oracle middleware, and even become a cornerstone of NFT financialization. But its problem is how to design this algorithm, how to assign weights, etc.
>>>3、Expert assessment pricing<<<
In CCTV's "Treasure Hunt" program, when faced with a collection, several senior personnel in the industry will evaluate it, and then collegially evaluate a price. We can learn from this idea:
For an NFT, a professional person evaluates it, and then formulates an evaluation rule (such as removing the highest, removing the lowest, and taking the average of the others) to determine the price of the NFT.
The advantage of this method is that it can more accurately reflect the value of each NFT (instead of being averaged by other NFTs), so that the value that he can use will be further released (for example, if the NFT over-collateralization in other ways requires 170%, Probably only 130% is needed this way)
>>>4、Competition pricing<<<
It's a word we coined. The idea comes from our currency price formation mechanism. The currency price is actually generated by the game of various traders in the market. So can we hand over price discovery of NFTs to traders in the market? One idea is:
We mentioned the idea of converting NFTs into homogenized tokens before, and then the homogenized tokens can be carried out according to the game of market participants, so that the price of NFT is equivalent to being discovered in real time, and we can also introduce AMM (automatic market making mechanism) to increase liquidity.
3、Project research
In the next work, we will study the projects on the market and improve our previous thinking.
We collected some projects in the market based on the above measures and pricing mechanism, and drew the following picture:

We will introduce some featured projects. While understanding the mechanism of the project, we will also verify and improve the previous thinking.
Note: If you are not interested in specific projects, you can skip this part
3.1 NFT trading platform
[What to do]: NFT trading platform is to provide traffic entry for buying or selling NFT
[Pricing mechanism]: Mainly manual quotation (buyout price), auction
Specific introduction:
At present, there are many NFT trading platforms, some are centralized and some are decentralized.
For example, there are Opensea, Looksrare, x2y2, etc. on the ETH chain. FTX and Binance have their own dedicated NFT trading sections. Other public chains are also building their own NFT trading platforms, so I will not list them all here.
Whether a trading platform can develop usually depends on several dimensions such as [first-mover advantage] [use experience] [transaction costs] [innovation model] [audience] [big environment].
3.2 NFT transaction aggregator
[What to do]: Aggregate NFTs on different platforms, which can be purchased or sold across platforms, while providing portable functions
[Pricing Mechanism]: The same as the trading platform, mainly manual quotation (buyout price), auction
Specific introduction:
The most famous ones are Gem and Genie, both of which provide NFT cross-platform aggregation transactions, and the "Batch Sweeping Floor" function is very useful.
Gem
Gem was born out of Vasa's innovative cross-asset swap system in 2021, an emerging NFT market aggregator, launched to the public in January 2022.
Additionally, Gem’s takeaway is that it allows traders to buy NFTs with any combination of ETH and ERC-20, so you can keep those DeFi tokens in your wallet and use them directly when buying NFTs without converting to ETH.
Currently, the project adds support for batch listing of NFTs and integrates liquidity with LooksRare. Meanwhile, Gem's new rarity ranking feature and collection analysis are especially useful for collectors.
Genie
Launched in November 2021, Genie is the first NFT market aggregator to enter the crypto economy. Currently, the project offers two main products: Genie Swap and Genie List.
Genie Swap is the platform's flagship marketplace aggregation service. Notably, it lets users swap combinations of ETH and NFTs (with available liquidity pools on NFTX and NFT20) to other NFTs, and it uses various optimizations to reduce gas costs.
Currently, Genie supports CryptoPunks marketplaces across OpenSea, Rarible, Larva Labs, and the exchange of the aforementioned NFTX and NFT20 liquidity protocols.
As for Genie List, the service allows users to list their NFTs simultaneously on multiple marketplaces (currently OpenSea and Rarible are supported), reaching the largest possible audience of potential buyers.
3.3 NFTX
NFTX
Related Links: Website, Documentation
[What it does]: A platform for creating liquid markets for illiquid non-fungible tokens
[Pricing Mechanism]: Game Pricing
3.3.1 Introduction
Users deposit their NFTs into an NFTX vault and mint a fungible ERC20 token (vToken) that represents a claim to random assets within the vault. vTokens can also be used to redeem specific NFTs from the vault.
- LPs and staking mint vTokens for yield rewards
- Better distribution and price discovery mechanisms for NFT projects
- Any NFT can be sold instantly by minting it as ERC20 and swapping it through Sushiswap
- Increase liquidity for NFT investors and speculators
3.3.2 Core content
- Convert NFTs to specific vTokens (fungible tokens), and then introduce AMMs, etc. to increase liquidity
- The price of NFT is initially set, and then the actual price discovery depends on the game of traders
- The main cost comes from the operations of minting and redemption
3.3.3 Process
- Create a specific vault, such as creating a BAYC vault
- Deposit a specific NFT into the vault to mint a specific vToken. For example, if I deposit a BAYC into this vault, I will mint a BAYC-vToken, which is 1:1 when minting, but because the minting process will A 5% fee is charged, so the actual BAYC-vToken obtained is 0.95
- Then you can add liquidity (the reserve price needs to be defined when it is first created), and conduct normal transactions or pledges
- If you want to redeem NFT, you need a BAYC-vToken for redemption. This redemption is random, that is, you may redeem any one of the BAYC vaults
- If directional redemption is required, then an additional 5% fee is required, that is, you need 1.05 BAYC-vTokens to redeem the NFT you want
3.3.4 DATA
3.3.5 Evaluation
- NFTX seeks growth by providing NFT-ERC-20 loans and on-chain liquidity. For loans, NFT holders do not have to give up ownership, and on-chain liquidity helps curb illiquidity and wash trading.
- Help NFT discover the real floor price
- It is useful for floor NFTs, not for high-value NFTs, but this problem can be partially solved by setting a specific vault for high-value NFTs
- NFTX helps to release the long-tail liquidity in NFT. From its data, its market has been developing steadily, and it has great development prospects in the future
- An interesting phenomenon is: NFTX’s token is NFTX, FDV is $57,741,271, and the amount pledged in the vault is $39,338,863, which are relatively close, indicating that the national treasury is very rich or the value of NFTX has yet to be discovered. Of course, one problem is that NFTX does not currently have its own token economics, which may come after it grows to a certain extent.
3.4 FloorDAO
FloorDAO
Related Links: Website, Documentation
[What to do]: Decentralized NFT market-making protocol, providing high-depth liquidity for NFT collections
[Pricing Mechanism]: Competition Pricing
3.4.1 Introduction
FloorDAO is a decentralized NFT market making protocol. It provides deep, sticky liquidity to all NFT collections included in the FloorDAO library. FloorDAO uses a bond and rebase mechanism pioneered by OlympusDAO to accumulate productive NFT liquidity, which is then deployed in strategies such as NFTX vaults to generate yield.
3.4.2 Progress

3.4.3 Token Economics
FloorDAO's token is $FLOOR
- FloorDAO has been fairly launched on the Token Liquidity Bootstrapping Pool (LBP) on the Ethereum mainnet on February 22, 2022 for its worthless governance token aFLOOR. There are no pre-sale or investors, and the initial funding for the auction comes from DAO-to-DAO loans from NFTX DAO.
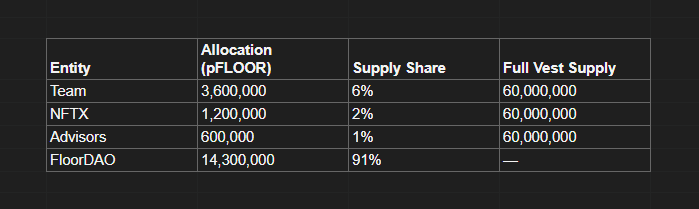
- For team incentives, FloorDAO follows the Olympus pOHM model and uses pFLOOR tokens for "supply share" vesting. pFLOOR is an options contract that allows the holder to exercise their limited right to mint FLOOR. To mint 1 FLOOR, holders must add 0.001 ETH to the FloorDAO treasury. This ensures that FLOOR remains intrinsically supported.
3.4.4 Evaluation
- At present, it mainly conducts in-depth cooperation with NFTX, and the main test object is blue-chip PUNK. If the model is successful, more blue-chip NFTs will definitely be introduced in the future. For NFTX, although he used the vToken method to convert NFT into a homogenized token, the next liquidity problem is still the most critical. Obviously NFTX also knows this, so he strongly supports the FloorDAO project start-up, provide financial support and advice.
- However, we also need to see one point: OlympusDAO's $OHM has already been in a death spiral, so what will happen to the future of $Floor based on this mechanism needs to be carefully considered.
3.5 Abacus
Abacus
Related Links: Website, White Paper
[What to do]: Provide pricing services for high-net-worth NFTs, so as to enable them to carry out DEFI, etc. to release liquidity
[Pricing Mechanism]: Expert assessment pricing
3.5.1 Core contentand Progress
A Session (an NFT pricing cycle) involves 3 parties:
- protocol
- Users who need to value NFTs
- Other users involved in valuation
1.First, users who need to value NFT pay ABC tokens worth 0.005 ETH to establish an NFT price evaluation session for the protocol. This part of the token is owned by the protocol and is the main income of the protocol.
2.Other participating users submit their own NFT price, random number (as the hash value of the submitted evaluation), and guaranteed amount to the agreement. The deposit is divided into three parts: 0.005ETH (minimal stake value, denoted as x) + 0.002ETH (Keeper tax, denoted as y) + 0.002ETH (bounty tax, denoted as z), the sum of the above three parts is 0.009ETH is the minimum amount submitted to the agreement by individuals participating in the NFT price evaluation
3.Calculate the evaluation price of NFT after the session expires. The calculation method is: the weighted sum of the prices of all NFT bids / the total number of votes. The weight calculation method is: the user's stake amount / the minimum stake amount of the entire session
4.Calculate the gain and loss to the NFT bidder. Simply put, the bidder's bid for NFT and the final valuation of NFT are less than 5% of the final valuation of NFT, and the reward will be awarded. The closer to the final valuation of NFT, the greater the weight of the user's income, and the weight is recorded as w
- The reward comes from the person who has a gap of more than 5% in the valuation of the NFT. The execution process is completed by Keeper. Anyone who participates in this bid can be used as a Keeper. The Keeper income is included in the deposit of each user's bid as 0.002 ETH.
- The profit of the bidder who gets the profit is: w * (x / total x) * the whole session profit
- The loss of the bidder who is penalized is: x * (% difference between bid and final estimate − 5%) * 𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑘 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟
The specific calculation method is:
a) If the difference between the bidder's valuation of the NFT and the final valuation of the NFT is less than 1%, the income multiplier will be 5
b) If the difference between the bidder's valuation of the NFT and the final valuation of the NFT is less than 2%, the income multiplier will be 4
c) If the difference between the bidder's valuation of the NFT and the final valuation of the NFT is less than 3%, the income multiplier will be 3
d) If the difference between the bidder's valuation of NFT and the final valuation price of NFT is less than 4%, the income multiplier 2 will be obtained
e) If the difference between the bidder's valuation of the NFT and the final valuation of the NFT is less than 5%, the income multiplier will be 1
5.Session ends
6.It should be noted that:
- Users who build a session can add bonuses when building a session as a way to motivate peers to bid
- The main income of the protocol is the ABC token of 0.005 ETH equivalent to the fee paid by each user who needs to value the NFT to establish a session. If the user also attaches a bonus when creating a session, the protocol will be executed during the session. You will also receive bounty tax, the total amount is the number of people who participated in the bid*y
- In order to prevent cheating, bidders cannot see the current voting status when voting in Session
3.5.2 Evaluation
- The Expert assessment pricing adopted by Abacus_wtf can more accurately value NFTs, and higher liquidity can be released after the price is accurate (for example, traditional NFT pledges can only pledge up to 33% of the value, while Abacus-based this The mechanism can even be pledged to 70% of the value)
- This mechanism is more troublesome for the pricing process of NFTs, which is not conducive to large-scale fast pricing, so we think it is more suitable for high-value NFTs.
- An obvious disadvantage of this mechanism is that if the NFT needs to be re-priced, it needs to re-convene a session and then re-evaluate, which obviously cannot form the continuous price of NFT.
3.6 JPEG'd
Related Links: Website, Related Information
[What it does]: Decentralized NFT lending protocol
[Pricing mechanism]: Algorithmic pricing, the algorithm mainly calculates the floor price
3.6.1 Introduction
JPEG'd is a novel and revolutionary lending protocol that will give NFT holders the opportunity to obtain credit for their assets while still retaining their ownership. The protocol is fully decentralized and governed by the token holders of the native platform. JPEG'd will also form multiple synergies with other protocols in DeFi to increase user-generated value. JPEG'd developed a creative insurance mechanism that allows depositors to buy back their NFTs from the DAO in the event of liquidation.
Pricing mechanism: algorithmic pricing, floor price. Sourced from a custom price oracle being built by partner Chainlink, it will provide the protocol with an ETH-based floor price.
3.6.2 Core Content
[Pledge]: The NFT is pledged into the vault and exchanged for PUSd. The DAO will initially provide liquidity for PUSd in a basket of other tokens in order to always keep its value as close to $1 as possible. Additionally, incentives will be provided to liquidity providers to add liquidity to this pool. This enables PUSd holders to easily exchange tokens to buy other cryptocurrencies or otherwise earn yields in DeFi.
[Interest Rate]: The interest rate is dynamically adjusted. The initial rate is 2%, the withdrawal fee is 0.5%, and the maximum allowable withdrawal is 32% of the value of the collateral. If it is higher than that, it will be liquidated.
NFTs are valued at their floor price, the above numbers do not necessarily represent the fair market value these NFTs will receive in the market, but they are the maximum amount of collateral we are willing to give them at launch. These numbers are important because it determines how much credit they can get. To reduce risk, we cap the collateral value at these levels at launch; however, governance can change these values later.
【Liquidation】: If it exceeds or equals 33% debt/equity ratio, it will be marked as liquidated. Only DAOs can liquidate. DAOs can choose to hold NFTs and sell them on the secondary market or over-the-counter market.
【Insurance】: A novel insurance mechanism. Users have the option to purchase insurance for a non-refundable 1% fee on their loan drawdowns. If they are liquidated, they can buy back their punks from the DAO after paying the debt, accrued interest, and a 25% liquidation penalty. The DAO underwrites all debt and ensures that the DAO can repay all outstanding debt and accrued interest at any time.
[Business scope]: Currently it is mainly PUNK, and will expand horizontally to all NFTs in the future, including EtherRocks, Art Blocks, Dino Pals, Autoglyphs, Bored Ape Yacht Club, etc.
3.6.3 Token Economics
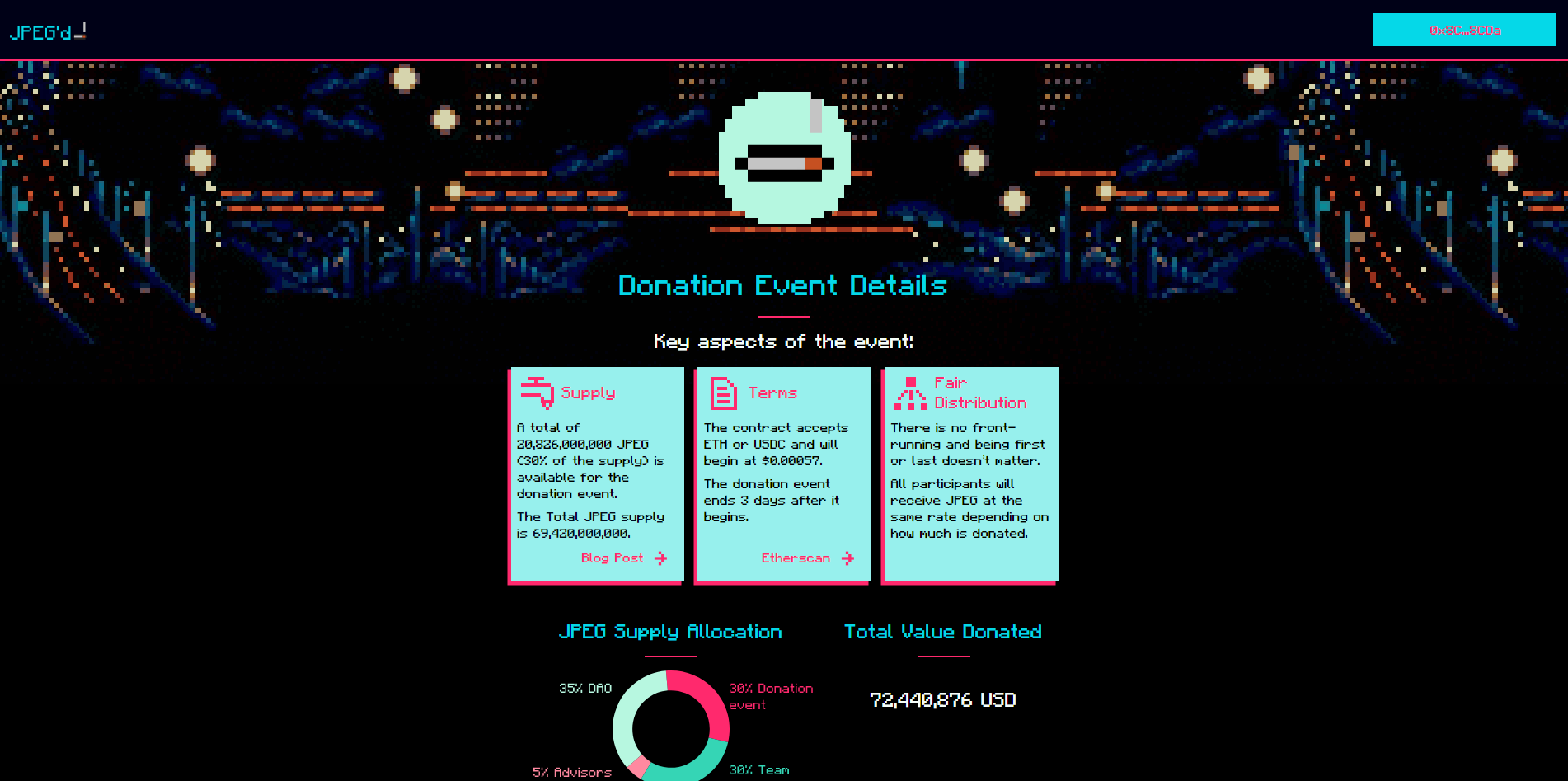
JPEG is a worthless governance token with no economic value. Its sole purpose is to govern the protocol’s utility token. In exchange for the exchange token to the DAO, you will receive a worthless governance token with zero profit expectations. The total supply of JPEGs is 69,420,000,000. Token splitting is shown in the following diagram:
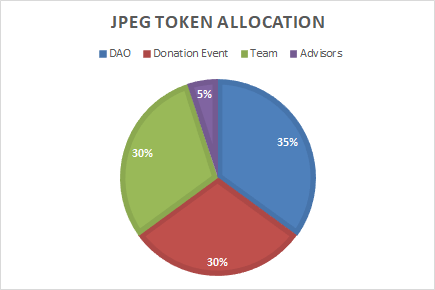
The project token is $JPEG
Total donations received: $72,440,876 Average price: $0.000378
Current FDV is: $141,843,590, Price is: $0.002043
3.6.4 Current Development
- Launch of Olympus Pro Bonds in partnership with Olympus DAO
- Working with Tokemak to Deepen JPEG Token Liquidity
- In partnership with Abracadabra Money, JPEG'd will launch a liquidity pool containing the Abracadbra protocol's stablecoin MIM
- In partnership with Dopex, on-chain options, plans to launch SSOV for JPEG tokens on Dopex. Users will be able to buy call options on JPEG using the liquidity pool and options management suite provided by Dopex, and we hope that PUSd minters can seamlessly use their NFTs as collateral to buy ETH call options (or other assets provided by Dopex).
3.6.5 Evaluation
- What is very novel is the quotation mechanism based on ChainLink. If successful, it will lay a solid foundation for NFT*DEFI.
- Another worth mentioning is the insurance liquidation mechanism he provides. In the traditional NFT lending market, if liquidation occurs, the user has no chance to redeem his NFT, but JPEG provides such an option.
- At present, FDV is on the high side, and the people who donate are basically deep-set, so it is necessary to observe the specific implementation of the project, and then evaluate it. The ChainLink-based price mechanism (TWAP) also needs to observe the effect.
- However, it can be seen that the project party is actively working to enhance liquidity. A problem can also be seen here. If there is a perfect continuous price mechanism, then there is basically no obstacle to the combination with traditional DEFI.
3.7 GRADIENT

Related Links: Website, Related Information
[What to do]: NFT-based DEFI lending protocol
[Pricing mechanism]: Algorithmic pricing, calculating the actual value of NFT
3.7.1 Introduction
Gradient is a DeFi lending protocol that allows instant lending using any NFT as collateral, while allowing anyone to earn from the NFTs they own.
Pricing mechanism: Algorithmic pricing. The protocol uses Abacus Spot to find the market price of your specific NFT in real time. As a result, your loan can be disbursed automatically and instantly, up to 85% of the value of the NFT.
3.7.2 Core Content
The traditional mortgage loan model, but because it can be accurately priced, can greatly increase the loan amount, even up to 85%.
Gradient is a non-custodial liquidity protocol. Backed by a Liquidity Pool (LP), loans are instant and never expire, allowing you to choose between stable or variable rates. You can also earn LP fees by providing liquidity (ERC20s).
The protocol is planned to be deployed on the Ethereum mainnet, Arbitrum and Optimism.
The most important point of this project is the Abacus Spot pricing mechanism adopted, and we will introduce this interesting pricing mechanism in detail.
3.7.3 Abacus Spot Introduction
Suppose Alice is the owner of the NFT/pool and Bob, Charlie and Denise are the traders.
Part 1: Create the pool
Alice creates a pool for her Cryptopunk.
- Named Ownership Token oPUNK
- The tokens in the named pool are PUNK
- The initial valuation of Punk is set at 100 ETH, so 1000 PUNK are minted at a token price of 0.1 ETH.
- Set an exit fee of 5%.
A dutch auction starts with a starting price of 0.1ETH per PUNK, if the initial supply sells out at 0.05ETH. Each bidder can now redeem their PUNK at 0.05ETH/PUNK. This means that Alice's PUNK is initially valued at 50ETH.
The mechanism of benchmarking the stock market is the reason why Abacus Spot works, and NFT owners are more inclined to add pools according to the actual value
Part 2: Transactions
After the pool is open for trading, Bob, Charlie, and Denise can start trading PUNK - AMM on their session-specific order books. There are no PUNKs in the pool, Charlie decides to mint 100 PUNKs, so he mints 100 PUNKs with a total price of 5.5ETH (each PUNK costs 0.055ETH). If they think PUNK is overvalued, they can sell their tokens to the pool, short the pool, or both! Sales are paid in tranches based on purchases. So if Dennis wanted to sell 150 PUNKs, 100 of them would be sold at 0.055 ETH (Charlie's mint price) and the other 50 at 0.05 ETH.
Part 3: Valuation
At any time, Alice or anyone interested can call the current price of NFTs held in the pool by looking at the ETH balance. Using this, Alice can bring her owner's tokens to the lending protocol and lock them up as a form of collateral.
Part 4: Closing
Mode 1 (Auction). Alice wants to sell her NFT, so she puts it up for public auction. The value of the NFT was locked in the pool at 80ETH, but it was sold for 100ETH. The two values are exchanged, so 100 ETH is received in the pool, 80 ETH is received by the owner, and the NFT is sent to the auction winner. Therefore, the principal of the token holders is returned, and the extra 20 ETH earned is distributed to them proportionally.
Mode 2 (exit). Alice wants to withdraw her Punk and decides not to risk losing it at the auction, so she pays an exit fee of 5%. If the value of the NFT is 80 ETH, Alice must pay the token holder 4 ETH to unlock her tokens. In this case, traders Bob, Charlie, and Denise receive their principal and split the fee based on each's proportion of ownership in the pool.
3.7.4 Evaluation
- As an NFT lending protocol, its main innovation is the adoption of a new pricing mechanism called Abacus Spot. If this mechanism can work well, Gradient will have an advantage as a pioneer.
- At present, the Abacus Spot core contract has been completed and is in the final internal testing stage. The team plans to conduct an audit with Halborn in the first week of March 2022, with the aim of launching on testnet in the coming weeks. What we need to do is observe the actual testing of the Abacus Spot and then make an evaluation.
3.8 PINE
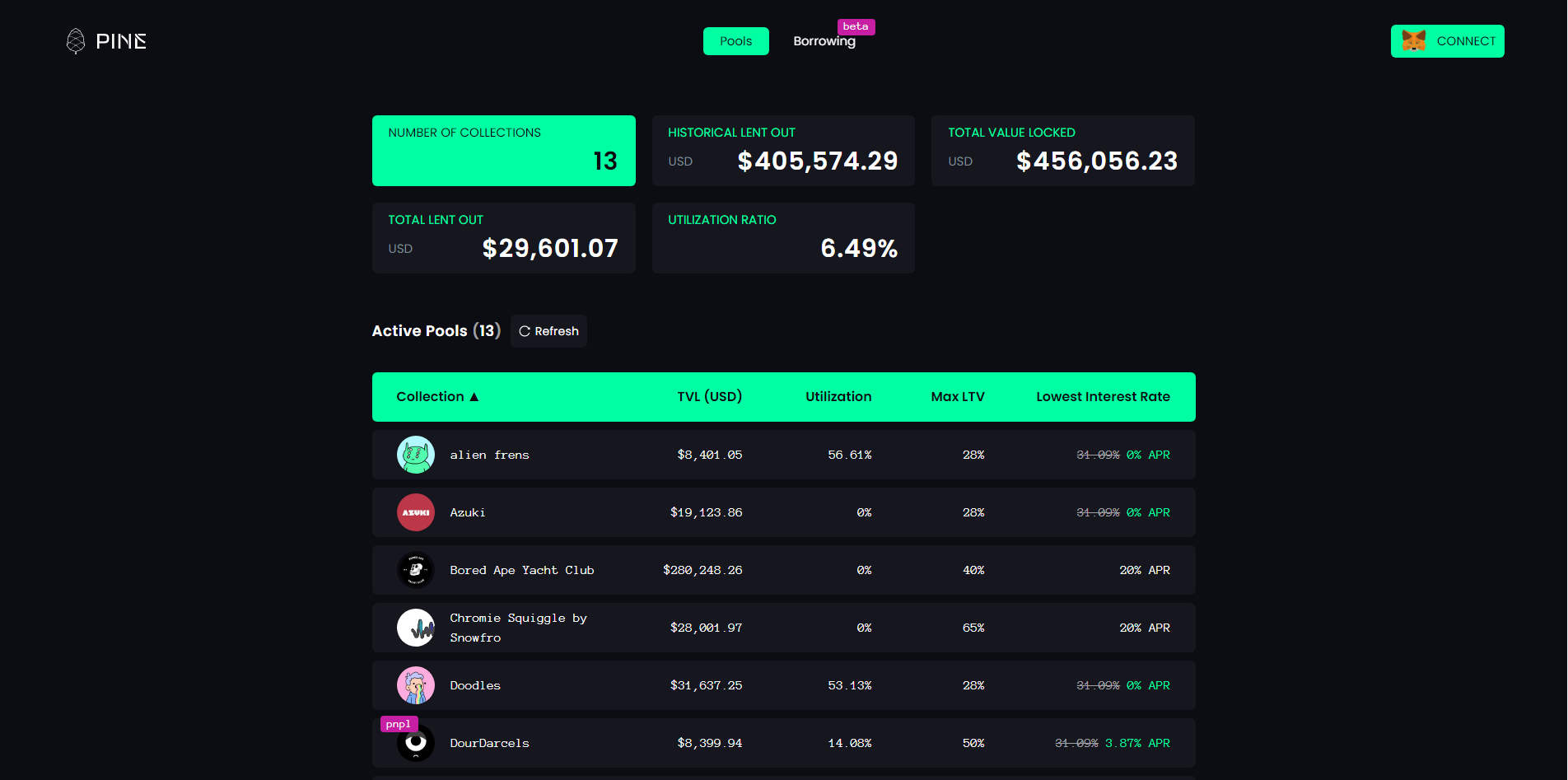
Related Links: Website
[What it does]: Decentralized lending protocol that supports NFT
[Pricing Mechanism]: Algorithmic pricing, calculating the floor price through an algorithm
3.8.1 Core content
- Regular mortgage NFT to lend ERC-20 tokens.
- Pricing Using techniques such as TWAP to smooth out price feeds to reduce risks associated with price manipulation, temporary fluctuations or short-term data feed failures, the alpha version calculates NFTs through min (7-day average transaction price, collect floor price) obtained from OpenSea via API s price. This should be the most emphasized [Permissionless] guarantee of the project.
- If the borrower fails to settle the loan obligations at the end of the loan term, i.e. repayment of the loan and accrued interest, the liquidation is done manually.
- Currently lending is only open to PineDAO and some whitelisted institutional lenders.
- Currently on the ETH chain, plans to support Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom….
3.8.2 Evaluation
Conventional mortgage NFT lending projects do not have much to offer. From the data point of view, TVL is very low, the loan amount and utilization rate are very low, and the future development is unknown.
3.9 PilgrimProtocol
Related Links: Website, Documentation, White Papers
[What it does]: An atomic valuation system for illiquid assets, a protocol designed to create liquidity for illiquid assets
[Pricing Mechanism]: Algorithmic Pricing
3.9.1 Core content
The whole thing is to put NFT mortgage into Pilgrim, and then borrow a batch of temporarily worthless liquid assets Round, which will make liquidity and price positively correlated according to Pilgrim's own algorithm, and at the same time have 0 slippage.
The specific way is that when Lister mortgages the NFT in Pilgrim, it will define the current loan position LBP internally, and then lend a batch of temporarily worthless current assets Round according to the LBP. Traditional mortgage loans usually have a fixed loan-to-value ratio LTV. , used to borrow a fixed percentage of liquid assets, where illiquid assets are designated as collateral with fluctuating values, valued through supply and demand bidding or public auctions. Pilgrim, on the other hand, allows for liquid collateralized borrowing positions with a fixed LTV, allowing the value of NFTs to be determined based on the valuation of their corresponding LBPs
This LBP is deformed according to the model of the AMM curve (A asset * B asset = a certain fixed value), and transformed into a dynamic liquidity provision model, so there are two more features.
- Increase the liquidity of LBP when the demand for the corresponding asset increases and vice versa
- Transactions are executed after liquidity is provided, achieving extremely low slippage
But at the same time, because every increase in demand (purchasing the NFT's Round) will be accompanied by the injection of basic tokens (ETH, PIL, stablecoins, etc.), the liquidity will also be adjusted according to the value of the liquid assets that have been locked through the mining pool contract. , so the price change has a positive correlation with the deposited liquidity, which is different from the price trend of Uniswap based on the supply and demand curve of tokens (the specific algorithm formula and principle are in Pilgrim's official valuation and algorithm paper)
And this protocol will be divided into 3 roles in operation:
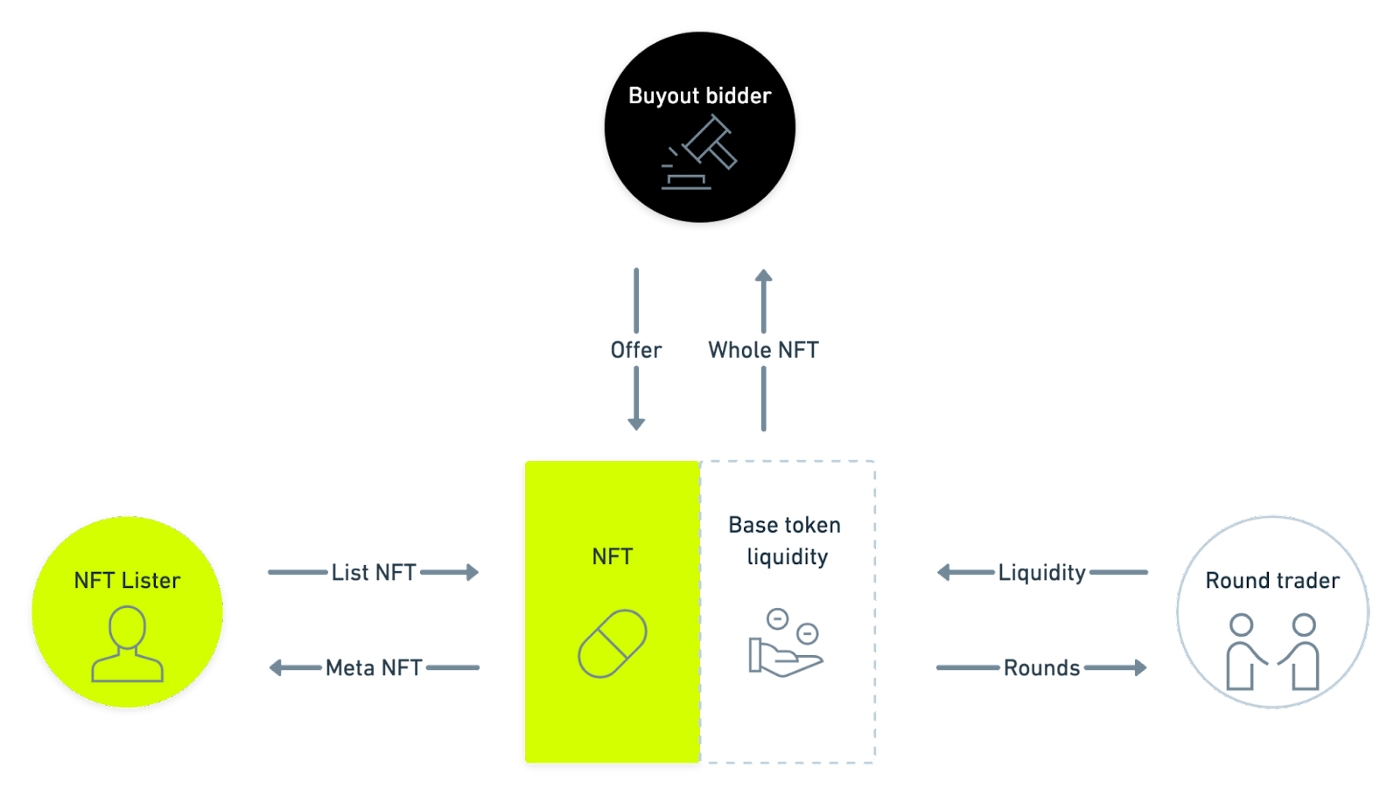
The first role is the lister of NFT/illiquid assets and the owner of the NFT's LBP - Lister
During the whole process, Lister will pledge to provide NFT and then obtain MetaNFT (the proof of ownership of the NFT's LBP is transferable and has the original NFT Metadata, so if you pledge Axie's NFT, you can continue to use this MetaNFT to play gold to generate income). The Lister who owns MetaNFT can have the following rights and interests
- Transaction procedures for obtaining NFT liquidity pools and incentives for PIL tokens
- Approve the buyout of NFT/MetaNFT, and then liquidate the corresponding LBP
The second is the Trader that trades the NFT liquidity pool
Trader acts as the liquidity provider of the NFT in the whole mechanism and also gives the NFT the role of pricing
They can exchange some of the NFT's liquid assets, Round, by injecting the basic tokens, and these Rounds are not ERC-20 tokens, so they cannot be transferred, and the Round does not have the Metadata of the NFT, so it does not count as holding the NFT. part of an NFT. However, this form allows users to benefit from trading the price of the NFT without purchasing the entire NFT, and at the same time, they can obtain the incentive income of PIL, and the income of PIL will be determined according to the following three points:
- The time the round holder owns the Round
- The ratio of the liquidity deposited by the holder relative to the total liquidity of the pool
- Proportion of this liquidity pool relative to all Pilgrim liquidity pools
The third role is the bidder for the ownership of this NFT - Bidder
Bidder is a person who wants to buy out the entire NFT or MetaNFT. There can be multiple Bids at the same time, but the Bid that Lister can accept must meet the following two conditions:
- Bid must be higher than the price of NFT/MetaNFT given by the current liquidity pool
- The Lister can only accept the bid (earliest) that satisfies the lowest timestamp value under the first item, and the Lister has no right to choose from multiple bids
If Bidder wants to buy the entire NFT, after the Lister accepts Bidder's Bid, it will force the liquidation of the entire liquidity pool and the funds paid by Bidder are distributed to the metaNFT owner and round owner according to a predetermined algorithm (the specific algorithm is as follows: Interested people can double its algorithm and valuation papers), MetaNFT will be destroyed, and the original NFT will be sent to Bidder
If Bidder wants to buy MetaNFT, the entire liquidity pool will not be liquidated, MetaNFT will only be transferred, and the funds paid by Bidder are also distributed to metaNFT owners and round owners according to a predetermined algorithm.
3.9.2 Token Economics
The main purpose of Pilgrim's native token $PIL is to serve as the basic anchor token of the NFT liquidity pool and to incentivize users. The fixed supply cap is 1 billion and will not increase. However, relative to the initial circulation, it is expected to be diluted by 40% within 4 years. % of the value of a single token, but the reward parameters are halved each year to control the release of tokens.
The distribution of tokens is roughly as follows:
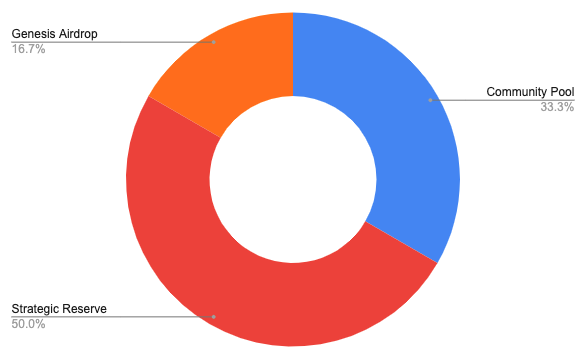
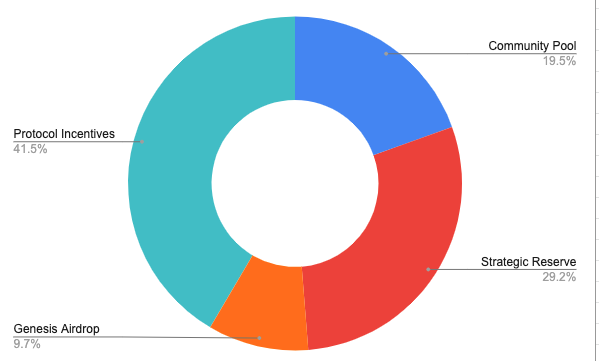
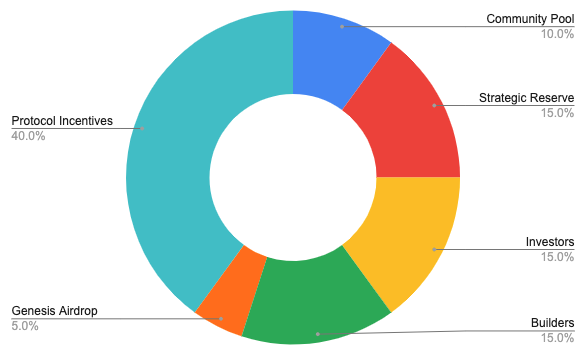
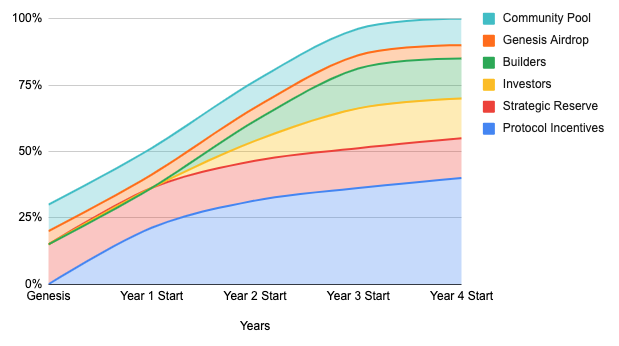
However, PIL does not intend to subject the holders of PIL to inflation, so it is necessary to make the lock-up amount of PIL tokens > the circulating output value of PIL to form a deflationary effect. For this purpose, Pilgrim has designed a series of measures to increase the demand of $PIL and reduce the circulation, which are roughly three routes:
- Using PIL as the basic anchor token in the NFT liquidity pool can get more PIL rewards, which will generate more PIL demand
- Become a PIL or xPIL liquidity provider on Uniswap to get more PIL rewards
- Stake PIL for 1 year to become an xPIL holder, you can get the repurchase of protocol income and participate in voting to govern PIL
The main source of income of the protocol is transaction fees, which are mainly from 3 sources:
- Round's transaction fee - 2 different fees are charged, the first is the base fee, which will be used to buy back PIL and distribute it to Round holders and xPIL pledgers; the second is the Round fee, which will charge Round Then distributed to holders of MetaNFT
- Buyout transaction fee for NFT or MetaNFT - used to buy back PIL and then distribute to xPIL stakers
- Cancellation of fees for listing NFTs in the Pilgrim protocol
Among them, Round’s transaction fees are expected to account for the largest share of the protocol’s revenue.
3.9.3 Evaluation
Pilgrim's algorithm is very novel. At present, it is the only one. We have gnawed on it and found that the formula involving the principle is still immobile. If you are interested, you can understand it. Generally speaking, we attach great importance to innovative projects. At present, we are observing the development of this project, and we will continue to update the relevant situation in the future.
3.10 Fractional_art
Related Links: Website, Related Information
[What to do]: A protocol for fragmenting NFTs
[Pricing Mechanism]: Competition Pricing
3.10.1 Introduction
Fractional is a decentralized protocol where NFT owners can mint tokenized fractional ownership of their NFTs. These tokens then function as normal ERC20 tokens to govern the NFTs they own.
Fractional is the leading project of NFT fragmentation.
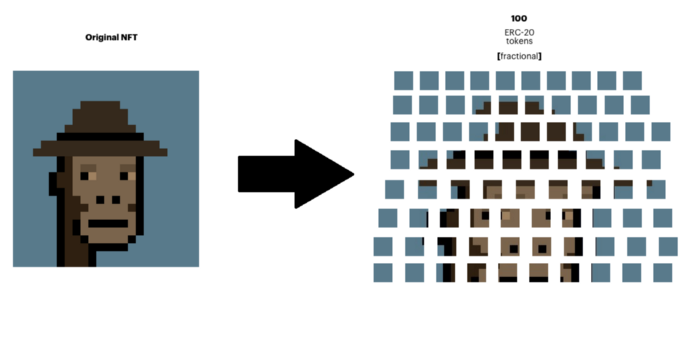
3.10.2 Core content
With Fractional, it will be easy to buy and own a percentage of NFTs. This allows users who were previously priced by certain NFTs or artists (such as Beeple) to be able to purchase their work. Among other things, subdividing NFTs allows the original managers of the NFTs to see some liquidity in their assets without selling the entire block.
Once users own a portion of the NFT, they have the right to vote on the asset's floor price. This floor price is the ETH price required by a third party to initiate the entire NFT auction. The floor price for new fractional ownership token collectors defaults to the current floor price, but can be changed at any time. After a successful auction, all fraction owners will be able to cash out their fraction in exchange for ETH.
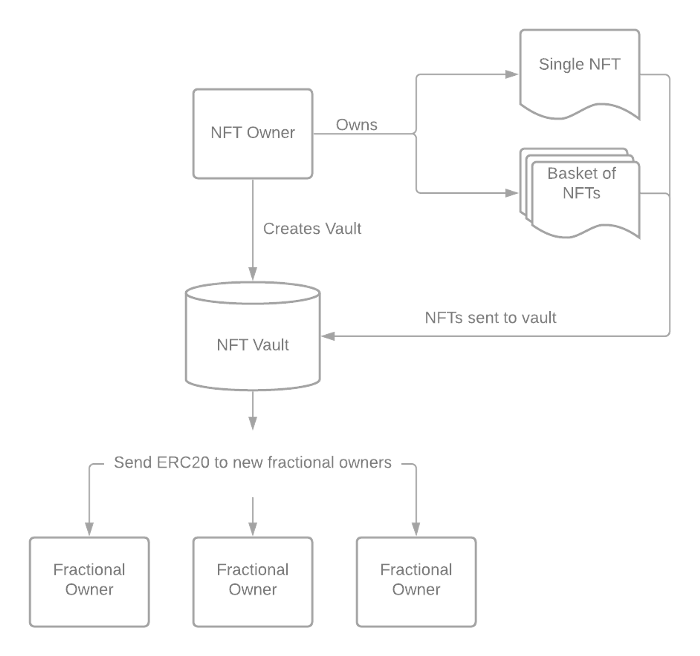
The operations after NFT splitting may include:
- Send them to friends to split and share ownership of NFTs
- Airdrop them to community members or owners of certain tokens
- Provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEX)
3.10.3 Evaluation
As the leader of fragmentation, the development of Fraction has a high probability of determining the future development of this subdivision track. Fragmentation, as a measure to improve liquidity, is mainly applicable to some high-value NFTs. At the same time, The issues of rights division and airdrops brought about by fragmentation also require careful consideration.
According to @RaccoonHKG's evaluation: His status as a fragmented leader is unquestionable, and the profit model and investors (Delphi, Paradigm...) are all qualified and above, but the valuation of the primary market has reached the sky, and the operating data has passed the golden period of growth, the best-case scenario of the second level can only get the industry Beta.
3.11 DefragFinance

Related Links: Website, Related Information
[What it does]: A decentralized NFT-based DEFI lending protocol
[Pricing mechanism]: Algorithmic pricing, using the average floor price
3.11.1 Core content
What this protocol features: Automatically insure your NFT assets using a financial instrument called a put option. In other words, in order to get a loan against your NFT, the protocol buys insurance on your behalf through put options.
The fragmentation and lack of liquidity of the peer-to-peer network led us to create an automated pool of option underwriting. The pool extends liquidity to borrowers without negotiating any terms with peers or counterparties.
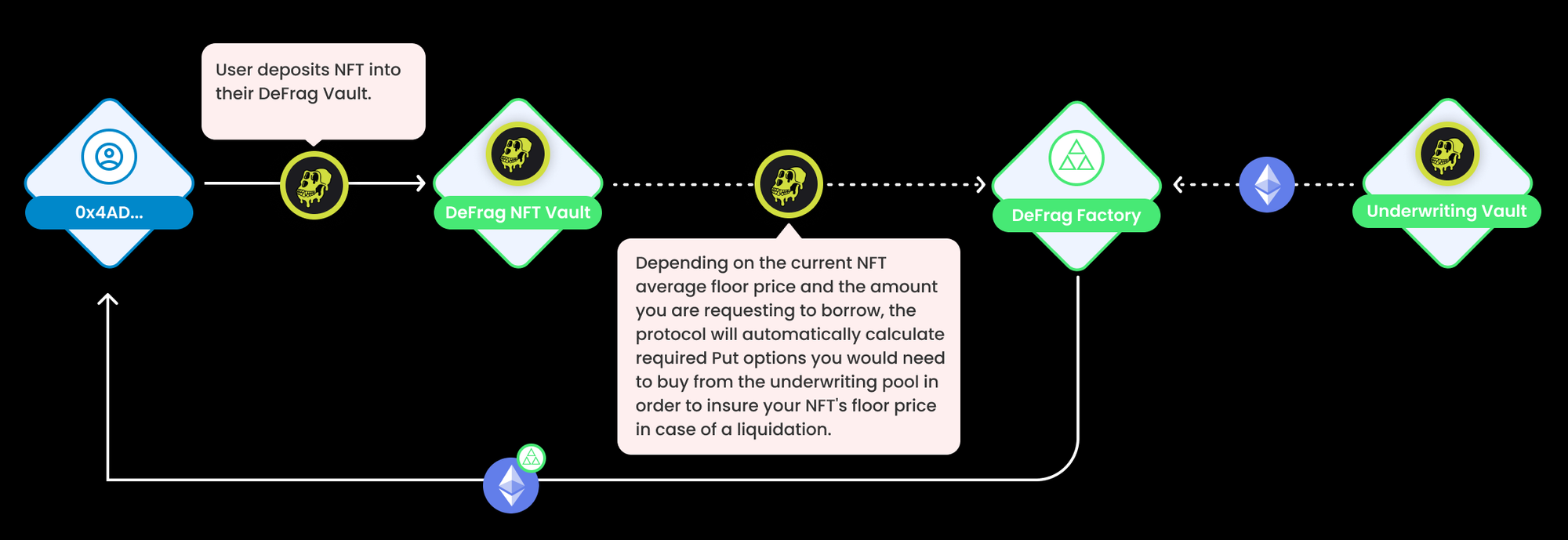
3.11.2 Progress
--loan
- Select the item you want to borrow. (eg Boring Ape Yacht Club)
- Create your DeFrag NFT vault and store your NFT assets. (eg Bored Ape #3547)
- Choose how much fETH you want to borrow (a sharded ETH synthetic version of the ETH generated by the protocol).
- Based on the current average floor price of NFTs and the amount you request to borrow, the protocol will automatically calculate the required put options you need to buy from the underwriting pool to secure the floor price of your NFTs upon liquidation.
- Issuance and selling of NFT put options occur automatically in the same transaction as borrowing. In fact, it is impossible to borrow unless a put option is issued.
-- liquidation
Similar to existing DeFi lending platforms, NFT collateral is liquidated by exercising put options once the average price of NFTs falls below a set liquidation price (set by the DeFrag DAO).
- Liquidity pools underwriting put options will lock ETH in case they need to be used to buy liquidated NFTs.
- Proceeds from NFT sales are used to close borrowers' outstanding loans.
- The purchased NFT is owned by the underwriting pool, so it is split into parts.
- Fraction is distributed proportionally among all underwriters who provide liquidity to the pool.
To provide a frictionless lending experience, the protocol needs to improve liquidity for underwriting loans
3.11.3 Evaluation
- The use of put options for liquidation is an interesting innovation.
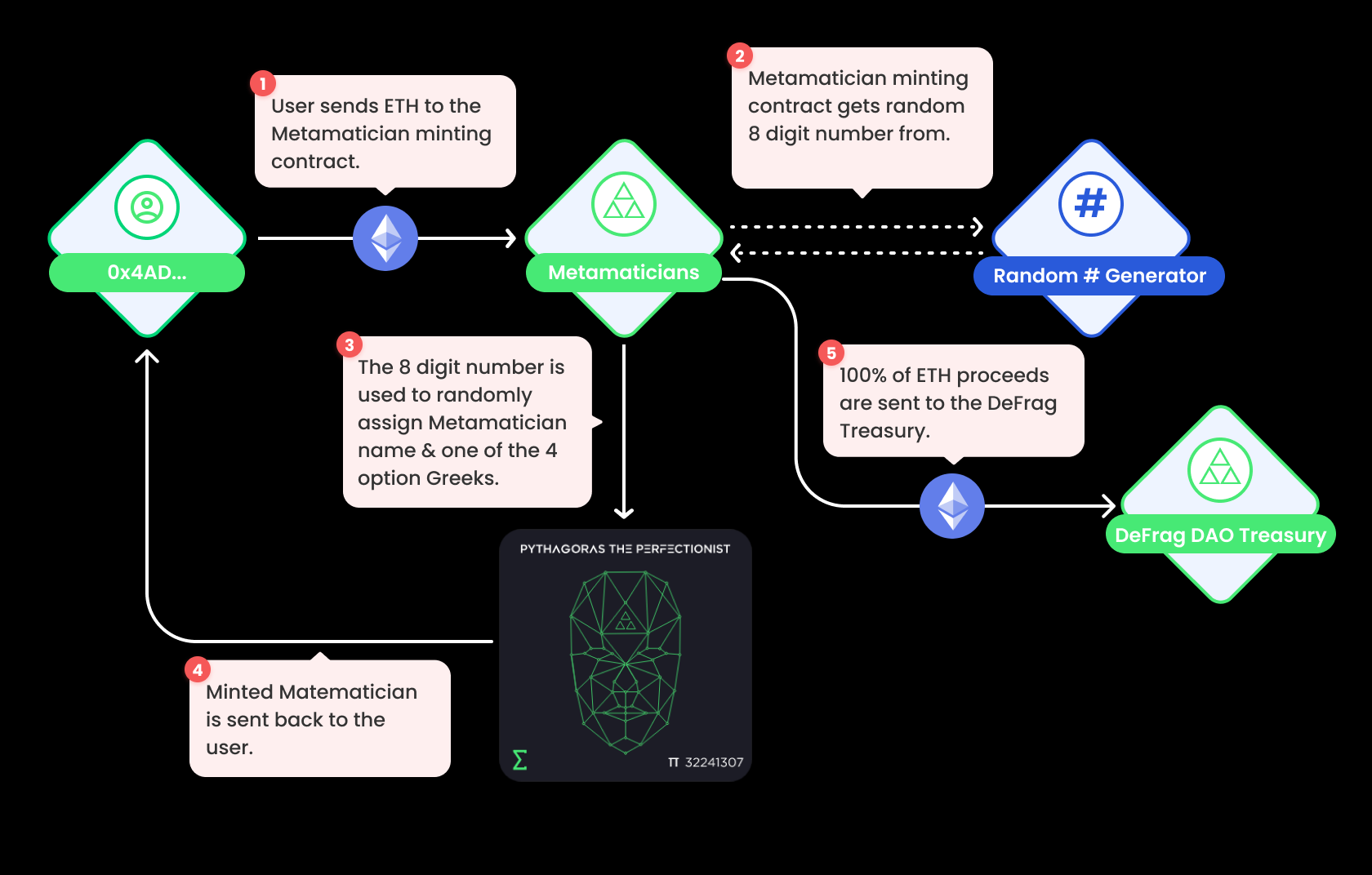
- The funds in the early stage of the underwriting pool come from the specific NFT issued, each 0.618ETH, a total of 6400. Currently, the progress of mint is very slow.
4、Our Opinion
4.1 Why choose this subject?
The NFT liquidity or more precisely the NFT*DEFI market is currently very small, which has a lot to do with "the current market value of the NFT market itself is not large" and "the NFT pricing mechanism is not perfect".
However, our group still chose to study this topic because of the following considerations:
- We believe that NFT will become a big piece of the puzzle in the Crypto world in the future, and the NFT market has a large space for development
- We have seen a huge change in liquidity after the introduction of DEFI in the currency circle, so this change will also happen to NFT in the future
- Holders of NFTs in the market have such a demand to manage and appreciate assets
4.2 What is the most important in improving NFT liquidity?
If we analyze from the current situation:
- The entry problem (that is, the trading platform) has been basically solved. There are many trading platforms, and the transaction aggregation will become more and more extensive.
- Introducing DEFI into NFT. The most important thing here is the pricing mechanism. Without pricing, DEFI is difficult to operate
So we believe that the most important thing at the moment is the "automatic oracle of NFT prices"
5、Reference
1、 @nichanank: Show me the Liquidity: Evaluating NFT Financialization Methods
3、The official website, white paper, Medium, Docs, etc. of each related project